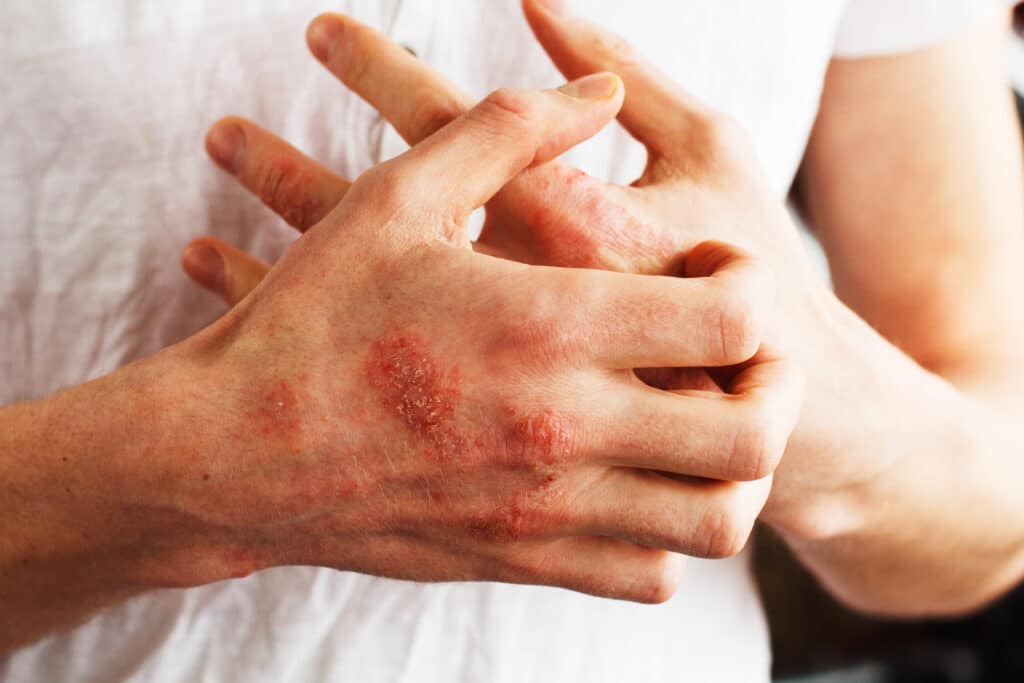
Are you struggling to find relief from the persistent itchy skin and irritation caused by eczema? You’re not alone. Millions of people worldwide are affected by this common skin condition, and it can be challenging to find an effective treatment that works for you.
I have a stark memory of using strong medical chemicals on my skin. The burning sensation caused me to wonder if it was improving or worsening my skin condition.
You’re here because you’re wondering the same thing: are there less harsh alternatives to modern medicine for my itchy, dry skin?
In researching and experimenting with various remedies for skin problems, I stumbled upon a natural alternative that has brought relief to the dry skin of many – apple cider vinegar (ACV).
This guide is perfect for those who have tried conventional treatments without success and are searching for a more holistic approach for healthy skin.
I’ll walk you through the benefits and potential risks of using ACV for eczema. I’ll share how ACV can potentially alleviate and treat eczema symptoms, along with the methods of application, precautions, and alternative treatments to consider.
So, let’s dive into the world of apple cider vinegar and explore how it may help you manage your eczema symptoms more effectively.
Understanding Eczema (Atopic dermatitis or atopic eczema)
Eczema is an umbrella term that covers several skin conditions, the most common of which is atopic dermatitis or atopic eczema.
In this section, I will discuss the causes and triggers, symptoms, and diagnosis of eczema, specifically atopic dermatitis.
Root Cause of Eczema: Weak Skin Barrier
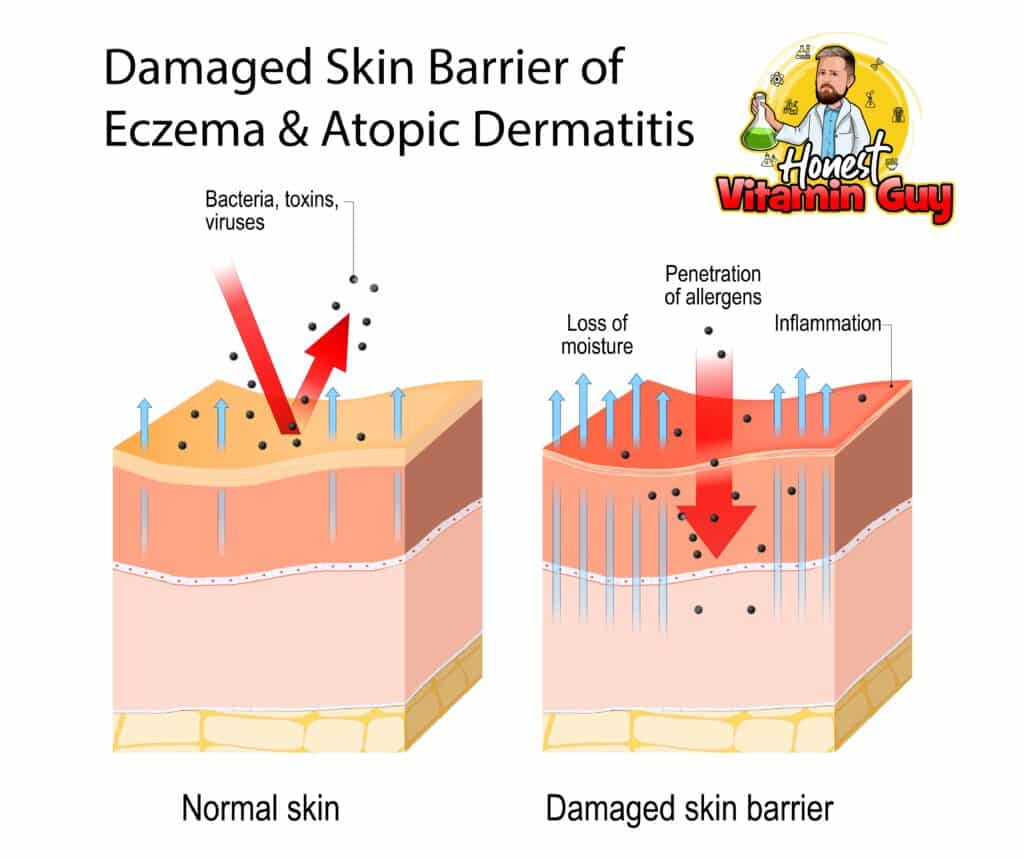
The root cause of atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a weak skin barrier.
Sometimes this weakness is caused by a genetic defect which causes chronic eczema typically.
Other times this weakened skin barrier integrity is caused by an excess of harmful bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus (staph bacteria). This harms the good bacteria of the skin bacterial microbiome.
This lack of healthy skin causes all sorts of problems because the skin barrier functions to keep bad stuff (viruses, toxins, bacteria, allergens) out and good stuff in (primarily moisture retention). Working to improve skin barrier integrity is one of the key goals of treating eczema.
Causes and Triggers
Some common triggers for eczema outbreaks include:
Bacteria
Environmental allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander
Temperature or humidity changes
Stress and anxiety
Irritants, such as harsh soaps and detergents
Food allergies, including eggs, dairy, and nuts
It is important to note that triggers can vary from person to person, so identifying and avoiding your specific triggers can help manage your skin irritation more effectively.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
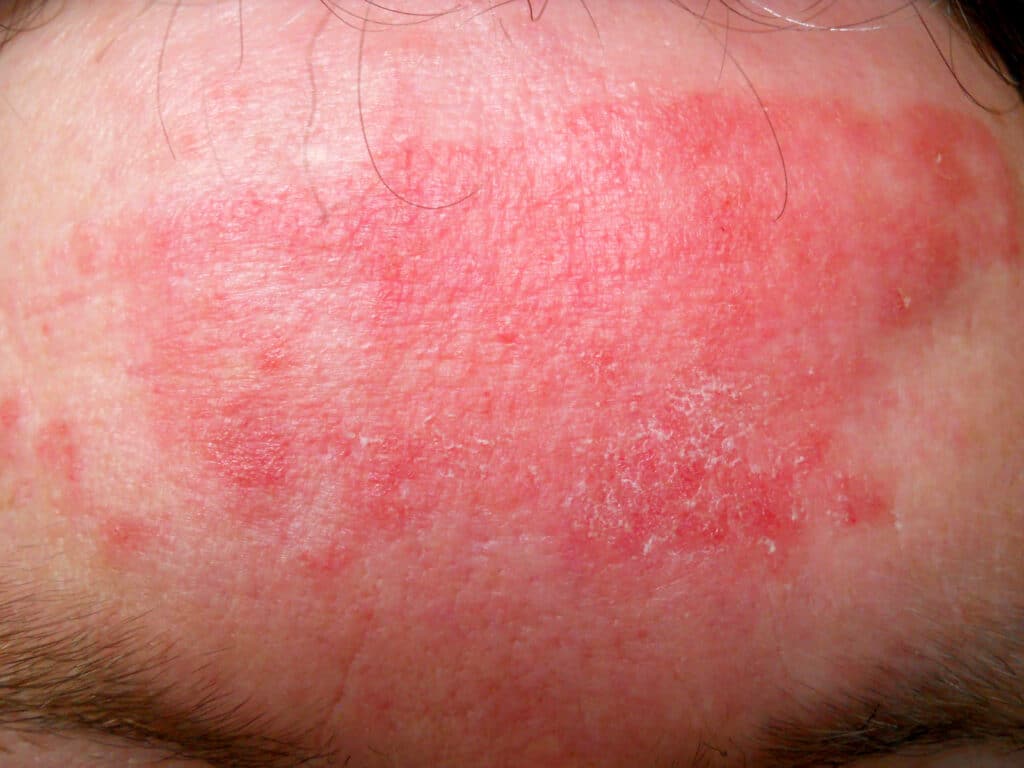
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) symptoms can differ significantly, but some common signs of the condition include the following:
Red, inflamed skin (this is your body fighting off the invaders)
Itchy skin
Dry, sensitive skin
Dark, discolored patches of skin
Rough, leathery, or scaly patches of skin
Oozing or crusting (in intense eczema flare-ups)
Diagnosing people with eczema is often based on a visual examination of the affected skin and information about your medical and family history. Your doctor may also perform a patch or allergy testing to help identify potential triggers and rule out other skin conditions.
Treating Eczema with Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is made from fermented apples and contains various nutrients and organic acids.
Acidic skin barrier
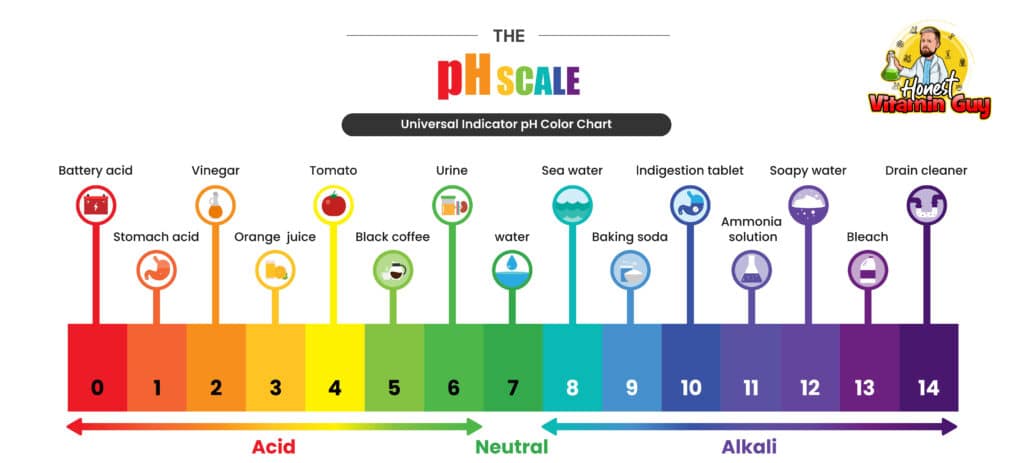
Apple cider vinegar is rich in acetic acid, which gives ACV its distinct sour taste and smell. One of the main health benefits of ACV lies in its ability to restore the skin’s natural pH levels. (According to one small scientific study, it positively affects it, but not for very long.) Eczema sufferers often have elevated pH levels, which can disrupt the skin’s protective barrier function.
Your skin barrier is slightly acidic. This acidity (the acid mantle) helps create a kind of buffer against the growth of harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi that could damage your skin and lead to infections and other skin conditions.
Soap is alkali or basic (it lowers the skin’s pH level) which is why many soaps irritate eczema further. Things that decrease skin’s acidity levels worsen eczema, while a mild acid like the acetic acid in apple cider vinegar can help reduce the skin pH levels to improve eczema by restoring the acidic skin barrier.
Anti-inflammatory and Antimicrobial properties
ACV also possesses antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
These attributes may help reduce inflammation, calm eczema-related irritation, and prevent skin infections.
Theoretically, apple cider vinegar should protect your skin’s microbiota by killing those foreign viruses and bacteria causing your body’s inflamed skin without harming your skin’s pH level the way soap does in people with eczema. However, one small study showed no effect.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While apple cider vinegar baths can offer the skin some benefits as a topical treatment for eczema, it is not without its risks and side effects. Undiluted ACV is highly acidic and can cause burns or irritation if applied directly to the skin. Therefore, diluting ACV with water before using it topically or by adding it to a bath is essential.
Additionally, some people might experience an allergic reaction to apple cider vinegar, so it is crucial to perform a patch test before applying it to larger areas of the skin. If you notice any redness, itching, or discomfort from apple cider vinegar, please stop using it immediately and consult your doctor.
In conclusion, apple cider vinegar has the potential to provide relief to some eczema sufferers due to its natural pH level re-balancing, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. However, it is essential to be cautious with its use, dilute it properly, and monitor your skin for adverse reactions. As always, please consult your doctor before you try new treatments for your skin condition.
Methods of Application

There are several ways to incorporate ACV into an eczema treatment routine. Some methods that I’ve found to be effective include:
Apple Cider Vinegar bath: Add a cup of raw, unfiltered ACV to warm bath water and soak the eczema for around 15-20 minutes of an ACV Bath.
Topical application: Dilute Apple Cider Vinegar with water in a 1:1 ratio and apply it to affected areas with a cotton ball as topical acids
ACV wet wrap: Wet a towel with diluted apple cider vinegar eczema for Apple Cider Vinegar soaks
Oral consumption: Drinking a teaspoon of ACV mixed with a cup of warm water daily may contribute to overall healthy skin
Precautions and Tips
Before using ACV for eczema treatment, there are a few precautions and tips to consider:
Always dilute ACV before applying it to your skin, as undiluted ACV can cause burns or damage sensitive skin.
Conduct a patch test on a small area of the skin to check for any adverse reactions before applying ACV to larger areas.
Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment, especially if you have a history of skin sensitivities or allergies.
Being cautious and mindful of these tips and precautions makes it possible to safely use ACV as part of a holistic approach to treat eczema.
Alternative Eczema Treatments
In this section, I will discuss some other alternative medicines and treatments for eczema, including over-the-counter solutions, prescription options, lifestyle changes, and home remedies.
Over-the-counter (OTC) Eczema Treatments
I suggest trying over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams for mild eczema, which can help reduce itching and inflammation. Additionally, I would look for moisturizers containing ceramides and hyaluronic acid, as they can support the skin’s barrier function to improve moisture retention.
Prescription Eczema Treatments
A doctor may prescribe stronger medications to treat eczema if it doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments. This may include topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors to help reduce inflammation and itchiness. In severe cases of eczema, systemic medications like oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be needed to manage your symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
Identifying and avoiding triggers can make a significant difference in managing eczema symptoms. Some common eczema triggers include:
harsh soaps & detergents
allergens
stress
In addition, to improve eczema symptoms I suggest wearing soft, breathable clothing, keeping your nails short to prevent scratching, and using a humidifier during the dry or cold season to help maintain healthy skin.
Home Remedies
You can also consider other home remedies, such as using oatmeal baths, dilute bleach baths, or aloe vera gel, which can provide soothing and moisturizing benefits to your skin.
Conclusion
Eczema is a prevalent and often distressing skin condition that affects millions worldwide. With various triggers and symptoms, it can be challenging to find an effective treatment.
Apple cider vinegar is a natural alternative that has shown potential in treating eczema due to its pH-balancing, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Apple cider vinegar is a mild acid that restores the skin’s natural pH level to fortify the acidic barrier.
ACV’s antimicrobial properties help restore the skin bacterial microbiome for healthy skin.
However, caution is advised when using ACV, as proper dilution is essential to avoiding acid burns.
While ACV may provide relief to some, it is important to consider other alternative treatments and consult a healthcare professional before embarking on any new treatment plan.
Ultimately, a combination of treatments, lifestyle changes, and understanding one’s unique triggers can help treat eczema once and for all!




